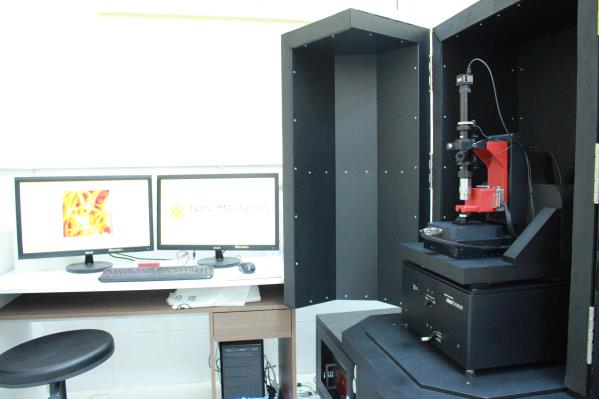
Atomic force microscope (AFM)
AFM solid or liquid surfaces Å It is a method used in topographic imaging at the level of Both conductive and non-conductive samples are measured in AFM. Flying in AFM; and atomic forces are detected between the sample. With the device, images with atomic size of the solid sample surfaces are obtained. "Sample surface, lift with needle tip; It is scanned continuously with a spring (ca
ntilever). Needle point interaction forces between the surface and the lever; It is kept fixed by the up and down movement of the spring and the movement of the spring is detected by sensitive optical systems and transformed into the image. Removeç The movement of the spring is detected by the incident of the laser beam, which is sent to and reflected from the bright arc surface, on the position-sensing photodiodes. AFM devices generally work in two different modes: These are; static (contact) mode and dynamic (tapping) mode.
Technical features of the device
· 16, 20 or 24 bits and 5, 10, 40, 100 μm XY scan range
· 16, 20 or 24 bit and 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 15 μm Z scan range
· 0.01 nm separation
· 10MP CCD Camera
· Optical Zoom
· 0.7 &micr;m optical separation
Applications Examined Materials
· Electronic Polymers
· Contact Ceramics
· Biology Composites
· Chemistry Windows
· Automotive Metals
· Energy Semiconductors